Inhalant drugs refer to substances and chemicals purposefully inhaled for a quick high. Inhaling everyday household products and chemicals is popular among young people and those looking for a fix during cravings when they cannot obtain the drug they seek.
The most common inhalants include:
- Volatile solvents or liquids that become gas at room temperature, like paint thinner, acetone, glue, gasoline
- Aerosol sprays like cooking spray, spray paint, deodorant
- Aerosol gasses like butane, propane, compressed air duster
- Nitrous oxide or laughing gas
- Nitrates which are also known as poppers on the party scene
Most people abusing inhalants don’t have a preference and will use whatever inhalants are available. In the United States, rates of inhalant abuse and related emergencies continue to increase. Experts are urging more studies about the long-term impacts of inhalants, addictive properties, and ways to treat inhalant use disorders effectively.
Are Inhalants Addictive?
Depending on the type of inhalant, addictive potential varies, but overall, inhalants can be addictive mentally and sometimes physically.
The National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) states that “a substance use disorder (SUD) develops when continued use of the drug causes issues, such as health problems and failure to meet responsibilities at work, school, or home.”
Inhaled substances give a quick high, causing users to take hits repeatedly to reproduce or prolong the mind-altering effects. Repeated inhalant abuse, or huffing, causes the brain to associate it with feelings of excitement and reward, causing psychological and physical cravings, both hallmarks of addiction.
In the United States and Australia, studies had found that toluene, a volatile solvent found in paint thinner, felt tip markers and certain glues, increased dopamine and serotonin activity when young adults inhaled. Dopamine and serotonin are chemicals responsible for pleasure and motivation; substances interacting with these chemicals have higher risk factors for abuse and addiction.
Inhalant Abuse Symptoms
Inhalant abuse symptoms may be challenging to recognize at first because the actual effects of inhalants are short-lived and because many common inhalants are household products already present in the home. However, the signs will be more evident as inhalant abuse becomes more regular.
Signs and symptoms of inhalant abuse include:
- Red or bloodshot eyes
- Frequent runny or bloody noses
- Chemical scented breath
- Clothes and personal items have chemical and paint stains and scents
- Stains from paint or markers on hands and around the mouth
- Red, cracked skin, or sores around the lips
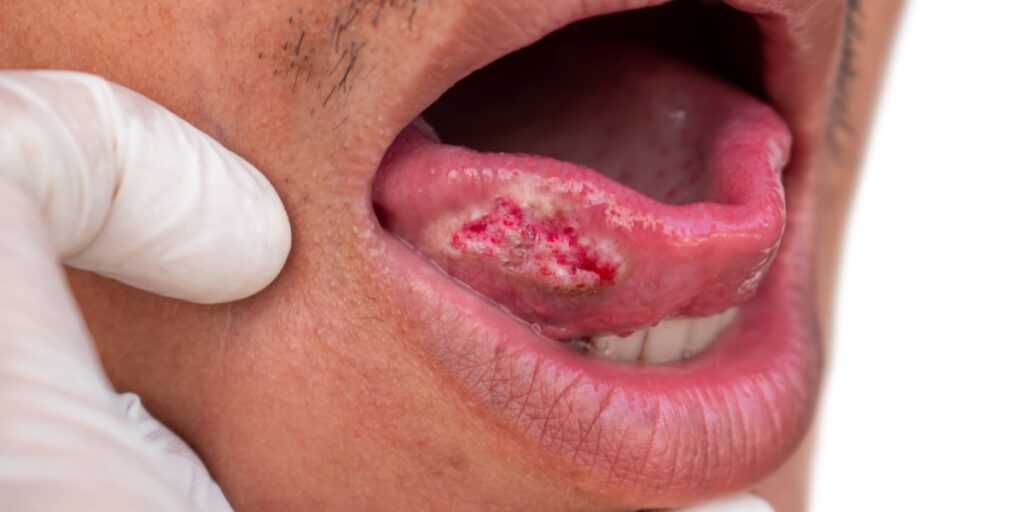
- Canker sores or open sores on the tongue and inside the mouth
- Sore or tender throat
- Noticeable changes in voice or frequent throat clearing
- Memory loss
- Confusion
- Agitation
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Mood swings
- Appetite loss
- Appearing drunk and uncoordinated
- Headaches
- Paranoia
- Slurred or slow speech
- Stumbling or walking differently
- Rags or bags with paint and chemical odors
- Empty canisters of spray paint, nitrous oxide, or other household products used for huffing
- Frequent purchases at places that sell common inhalants
- Double or blurry vision
- Involuntary eye movement
- Disrupted sleep patterns
According to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH), adolescents and young adults between 12 and 20 are the most likely to abuse inhalants in the United States.
Adult inhalant abusers typically fall between the ages of 35 to 49. Friends and family of young inhalant users tend to dismiss their behavior changes as typical teenage moodiness. Older users are usually self-aware enough to hide their habits better or abuse other substances that obscure the inhalant effects.
Trusting your instincts and talking to your loved ones when you notice signs of inhalant abuse is essential. Talk to other people in your circle to compare observations; it may be necessary to hold an intervention and help your loved one find a treatment program.
Side Effects of Inhalants
Thousands of substances are used as inhalants, so it is impossible to predict all of the side effects. Although all of them share the traits of displacing oxygen from the lungs and interacting with the central nervous system, therefore, share various common side effects.
Side effects of inhalants include:
- Lightheadedness
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Loss of coordination
- Blacking out or losing consciousness
- Fits of laughter
- Hallucinations
- Slow or slurred speech
- Lowered inhibitions
- Slow or delayed reflexes
- Increased heart rate
- Hypoxia, or low oxygen in the blood
- Headache
- Chest pain
- Coughing
- Shortness of breath
- Lethargy
- Twitching
- Seizure
- Stupor
- Coma
- Death
Nitrous oxide overdoses are sometimes treatable but still very dangerous; other inhalant overdoses, or sudden sniffing death syndrome (SSDS), are nearly always fatal. Inhalant overdoses happen equally to first-time and long-term inhalant users.
Inhalant Long-Term Effects
The long-term effects of inhalants can develop over time or after one use. The chemicals from inhalants can linger in the body long after the quick high wears off to cause physical and mental health problems that escalate with repeated use.
The long-term effects of inhalants include:
- Scarring in the mouth, esophagus, and lungs
- Chronic respiratory infections
- Bone marrow damage
- Kidney damage
- Heart damage
- Critically low vitamin B12 levels
- Brain damage
- Memory loss
- Hearing loss
- Vision loss
- Heart failure
- Paranoia
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Impaired learning
- Weight loss
- Muscle loss
- Muscle twitching and spasms
- Anemia
- Ulcures
The brain damage caused by chronic inhalant abuse is similar to alcoholic brain damage seen in people with severe alcohol use disorders.
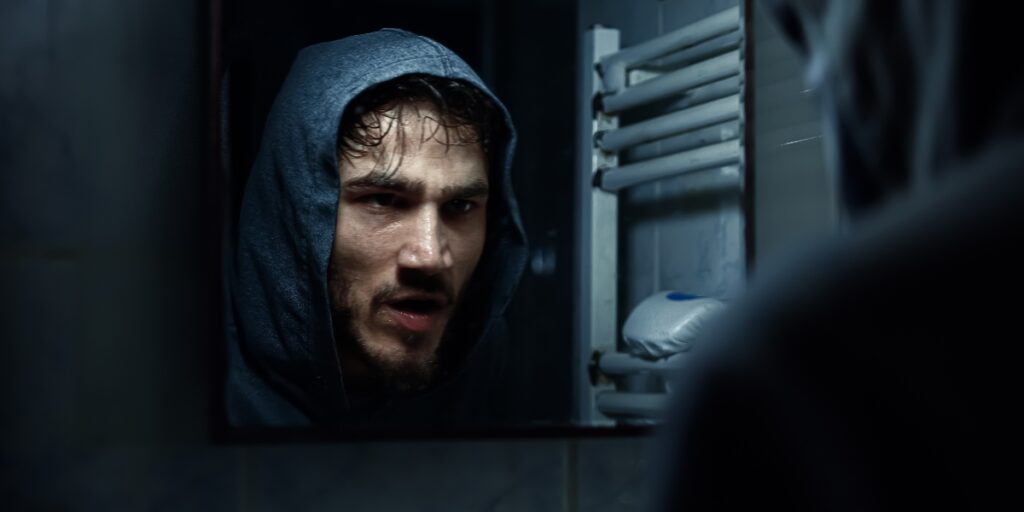

Inhalant Withdrawal Symptoms
As previously mentioned, there is a wide variety of inhalants, and withdrawal symptoms from inhalants will vary based on the substance of choice, the length and severity of abuse, and any pre-existing physical or mental health problems.
Inhalant withdrawal symptoms may include:
- Intense cravings for inhalants
- Mood swings
- Outbursts of anger
- Sweating
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Restlessness
- Muscle cramps and twitching
- Difficulty sleeping
- Decreased attention span
- Difficulty concentrating
- Stomach cramps
- Rapid heart rate
- Chest pain
- Nausea
Inhalant Addiction Treatment
Effective and genuine treatment is available if you are struggling with inhalant drug abuse and addiction. At Northridge Addiction Treatment Center, we specialize in treating the whole person with an evidence-based approach using dual diagnosis and various therapies to treat the entire person, not just the symptoms.
NATC’s licensed, experienced, and compassionate treatment specialists work closely with each resident to develop a personalized treatment plan for your unique needs and circumstances. NATC can help you build the confidence, knowledge, and skills to live an addiction-free, meaningful life.
Contact us now to begin your path to recovery. Our treatment specialists are eager to assist you.













